Session State In ASP.NET
Session State is one of the important state management variable in Asp.Net. It’s working on server side. Advantage of session state is that once you store your data in session and access that data from anywhere in the application across multiple pages. Advantage of session state over cookies is that session can store any type of data as well as complete dataset whereas cookies can store only small amount of data.
When you use session then session create a cookie on browser that name is Asp.Net_SessionId to detect correct user to provide associate information across multiple pages. Session state store user information on Web server not on browser like cookies.
Create Session
A new session can be created by specifying session name in session variable. For example, in below code we are creating a new session that name is UserName. In this session, we are storing simply a string value programidea. You can store any type of object data in session state.
Read Session Value
Once you created session then, you can retrieve stored object in session from anywhere in the application. Use below code to retrieve your session data from any page in the application.
if (Session["UserName"] != null)
{
string userName = Session["UserName"].ToString();
Session End
You can stop user session any time in the application. You have three option to stop user session.
1. Abandon - End user session in the application.
2. Remove - Remove a particular session in the application.
3. Clear - Clear all session object.
// Remove UserName session
Session.Remove("UserName");
// End a user session
Session.Abandon();
// Clear all session items
Control Session Timeout
When you are using session then session will expire after specific time. This time is known as session timeout. Default session timeout value is 20 minutes. But you can increase session timeout using session's TimeOut propery by declaring on page or in Web.Config.
<system.web>
<sessionState timeout="60"
/>
Disable Session
If you want to disable session then you can disable session from page or from Web.Config.
On page directive use EnableSessionState to false.
In Web.Config file set session mode Off.
<system.web>
<sessionState mode="Off"
/>
Session Property
Session state have following properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| CookieMode | Enable to you to specify whether cookieless sessions are enabled. |
| TimeOut | Enable to specify session timeout in minutes. |
| SessionID | Retrieve unique session id. |
| IsNewSession | Check session is new one or not |
| Count | Retrieve total session items from session state. |
| IsReadOnly | Check session is read only or not |
| IsCookieless | Check whether session is cookieless or not. |
| Keys | Retrieve all session items from session state. |
Demo:
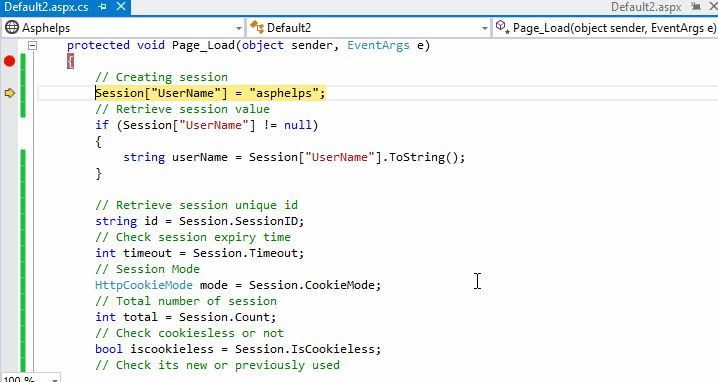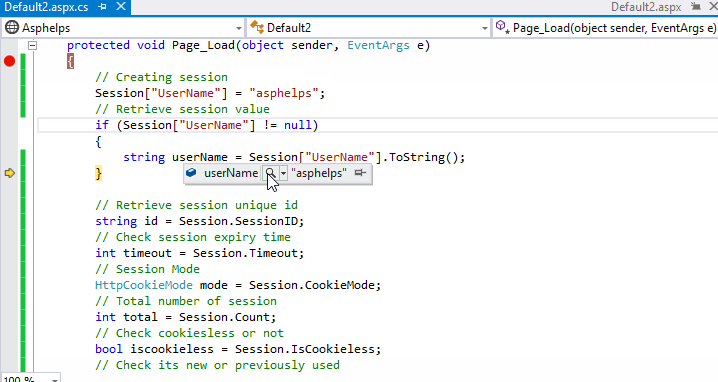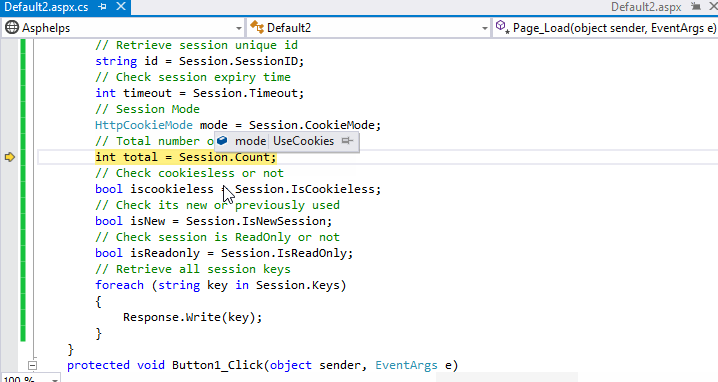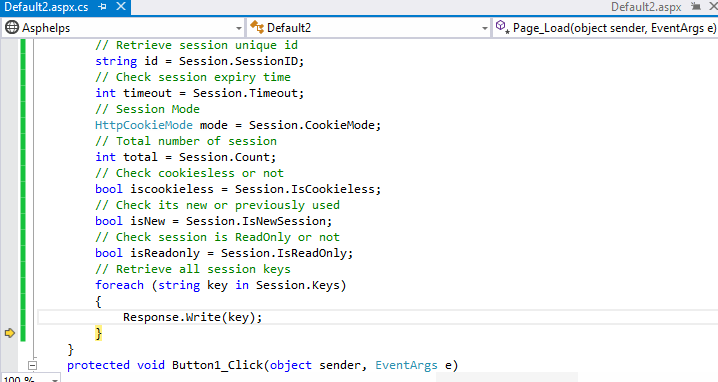
Session Configuration
You can set all session properties in Web.Config
<system.web>
<sessionState
cookieless="false" mode="InProc
"
timeout="60"
regenerateExpiredSessionId="true"
/>
Session Mode
Session state stores session data in multiple location that depends on session mode. You should know about session mode, so that you can use appropriate mode to store session data. Session have followings modes:
| Mode | Description |
|---|---|
| InProc | Session state stores session data on web server. This is default value. |
| Off | Disable session state in the application |
| Custom | Session state stores session data on custom storage location. |
| SqlServer | Session state stores session data in sql server database. |
| StateServer | Session state stores session data on separate process Session disable form page. |
Cookieless Session
Session state internally uses cookies to store user information. Asp.Net framework uses Asp.Net_SessionId cookies to identify user, so that specific user information associate with correct user.
Every browser providing cookies enable disable facilities. Suppose if any user disables their cookies on browser then session state does not work. In that condition you can take advantage of cookieless session that store user session Id in page url instead of cookies. So you session is working even if cookies is disabled from browser.
Its look likes below url:
For enable cookieless session, you have specify in Web.Config. Use cookieless attribute of sessionstate in Web.Config.
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| AutoDetect | Session state stores session ID in cookie when cookies enable on browser otherwise its add session ID in page url. |
| UseCookies | Always session state stores session ID in cookies. |
| UseDeviceprofile | Session state stores session ID in cookie when cookies enable on browser otherwise its add session ID in page url. |
| UseUri | Always session state stores session ID in page url |
We suggest you that use autoDetect, because its add session Id in page url when cookies disabled on browser otherwise its uses cookies.
Here we demonstrating that how cookieless session is working when you disable cookies from browser. First we are using normal session and after that we will disable cookies from browser and see how cookieless session will work.
Demo:
Use regenerateExpiredSessionId for better security purpose.
<system.web>
<sessionState
cookieless="AutoDetect"
regenerateExpiredSessionId="true"
/>
Session Event
Session State have two events that raised in global.asax
1. Session_Start
2. Session_End
Session_Start fires after whenever a new session is starts in the application and Session_End fires after whenever session abandoned or expired.
void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Code that runs on application startup
Application["TotalSession"] = 0;
}
void Session_Start(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Code that runs when a new session is started
Application.Lock();
int count = Convert.ToInt32(Application["TotalSession"]);
Application["TotalSession"] = count + 1;
Application.UnLock();
}
void Session_End(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
// Code that runs when a session ends.
// Note: The Session_End event is raised only when the sessionstate mode
// is set to InProc in the Web.config file. If session mode is set to StateServer
// or SQLServer, the event is not raised.
Application.Lock();
int count = Convert.ToInt32(Application["TotalSession"]);
Application["TotalSession"] = count - 1;
Application.UnLock();
We used Lock and UnLock application object because multiple user could potentially access the same item in the application state at the same time.